Biology
Biology is the branch of science that deals with life and living organisms. The main objective of Biology is to understand the various processes taking place inside any living organism. It includes the formation of cells, composition of cells and formation of tissues. It also reflects on the changes occurring in human body. It depicts how the living and non living components interact with each other.
Here we will cover the various topics regarding Biology for Class 9. The concepts that are mastered in the lower classes help us to crack many entrance examinations like NEET, AIIMS, AIPMT, UPSC etc. At ABHYASONLINE.IN you can master the concepts at your own learning pace. It provides conceptual testing with analytical reports identifying the weak, moderate and strong concepts. We, at ABHYASONLINE.IN believe that, if the weak concepts are timely identified and improved, then every student can achieve their goals in life. Follow the links below to understand and master each and every concept of various topics in Biology along with video lectures.
Explore Chapters
A Cell is the structural and functional unit of life. Cell is a building block with which all living organism are made, Cell is the smallest unit of life. The various topics that you will find in the links below are cell, how cell was discovered , structure of cell, functions of cell. We have discussed about the type of organism i.e. unicellular and multicellular, cell wall, plasma membrane, cell organelles and many more interesting topics
- Sample Test(s)Test NameSubject(s)Topics / ChaptersQuestions / MarksActionMOCK (F) - 9th - Biology [Fundamental Unit of Life I, Fundamental Unit of Life II]BiologyFundamental Unit of Life I, Fundamental Unit of Life II10 / 10Tutorial - 9th - Biology [Fundamental Unit of Life I]BiologyFundamental Unit of Life I10 / 10View All FREE Test(s)
A Cell is the structural and functional unit of life. Cell is a building block with which all living organism are made, Cell is the smallest unit of life In this section Topics such as protoplasm, cytoplasm, Endoplasmic reticulum, Ribosomes, Mitochondria, Golgi body, Plastids, Lysosomes, Centrioles, Cytoskeleton, Vacuoles, Nucleus, Chromosomes, Plant Cell, Animal Cell, etc. have been explained. Watch the videos and master the concepts
- Sample Test(s)Test NameSubject(s)Topics / ChaptersQuestions / MarksActionMOCK (F) - 9th - Biology [Fundamental Unit of Life I, Fundamental Unit of Life II]BiologyFundamental Unit of Life I, Fundamental Unit of Life II10 / 10Tutorial - 9th - Biology [Fundamental Unit of Life II]BiologyFundamental Unit of Life II10 / 10View All FREE Test(s)
In biology, a tissue is defined as a group of cells with similar structure, organized to do a common function. A tissue is a group of similar cells and their extracellular matrix to carry out a specific function. Organs are then formed by the functional grouping of multiple tissues. In this section topics of Plant Tissue such as Permanent Tissue, Parenchyma, Collenchyma, Sclerenchyma, Epidermis, Phloem Xylem, etc. have been explained. Watch the videos and master the concepts
In biology, a tissue is defined as a group of cells with similar structure, organized to do a common function. A tissue is a group of similar cells and their extracellular matrix to carry out a specific function. Organs are then formed by the functional grouping of multiple tissues. In this section topics of Animal Tissue like Blood as Fluid Connective Tissue, Cardiac Muscles, Connective tissue, Epithelial tissue, Fluid Connective Tissue, Lymph as Fluid Connective Tissue, Muscular tissue, Nervous tissue, Skeletal Connective Tissue
The biological world consists of many diverse species. There are so many varieties that it is almost impossible to study all of them in a single life span. Organisms have been grouped together on the basis of their features .In this section of diversity of living organism Classification, Classification depending on evolution, Taxonomic hierarchy, Taxonomy, Algae, Angiosperms, Animalia, Bryophyta, Charles Darwin, Fungi, Gymnosperms, Hornworts, Liverworts, Monera, Monocotyledons and Dicotyledons, Mosses, Plantae, Protista, Pteridophyte etc. have been explained. Watch the videos and master the concepts
- Sample Test(s)Test NameSubject(s)Topics / ChaptersQuestions / MarksActionTutorial - 9th - Biology [Diversity in Living Organism I]BiologyDiversity in Living Organism I10 / 10View All FREE Test(s)
The biological world consists of many diverse species. There are so many varieties that it is almost impossible to study all of them in a single life span. Organisms have been grouped together on the basis of their features .In this section of diversity of living organism Bacteria, Phylum Annelida, Phylum Arthropoda, Phylum Aschelminthes- Nematoda, Phylum Cnidaria Coelenterata, Phylum Platyhelminthes, Phylum Porifera, Viruses etc. have been explained. Watch the videos and master the concepts
- Sample Test(s)Test NameSubject(s)Topics / ChaptersQuestions / MarksActionTutorial - 9th - Biology [Diversity in Living Organism II]BiologyDiversity in Living Organism II10 / 10View All FREE Test(s)
The biological world consists of many diverse species. There are so many varieties that it is almost impossible to study all of them in a single life span. Organisms have been grouped together on the basis of their features. In this section of diversity of living organism Class Amphibia, Class Aves, Class Chondrichthyes, Class Cyclostomata, Class Mammalia, Class Osteichthyes, Class Reptilia, Phylum Chordata, Phylum Echinodermata, Phylum Hemichordata, Phylum Mollusca, Subphylum Cephalochordata Protochordata, Subphylum Urochordata Protochordata, Subphylum Vertebrata etc. have been explained. Watch the videos and master the concepts
- Sample Test(s)Test NameSubject(s)Topics / ChaptersQuestions / MarksActionTutorial - 9th - Biology [Diversity in Living Organisms III]BiologyDiversity in Living Organisms III10 / 10View All FREE Test(s)
In 19th Century man realized that his way of living and the environment around him affected his health and by controlling these factors he could prevent certain diseases In this section of Why Do We Fall Ill Acute and Chronic Diseases, Balanced Diet, Basic Conditions of Good Health, Causes of Diseases, Clean Air, Clean Food and Water, Clean Surroundings, Diseases, Eliminating Infectious Agents, Exercise and Relaxation, Good Economic Conditions, Good Health, Infectious Diseases, No Addiction, Personal Hygiene, Signs and Symptoms of a Disease, Spreading of Communicable Disease, Spreading of Communicable Disease Through Air, Through Body Fluids,etc. have been explained. Watch the videos and master the concepts
- Sample Test(s)Test NameSubject(s)Topics / ChaptersQuestions / MarksActionTutorial - 9th - Biology [Why Do We Fall Ill I]BiologyWhy Do We Fall Ill I10 / 10View All FREE Test(s)
In 19th Century man realized that his way of living and the environment around him affected his health and by controlling these factors he could prevent certain diseases In this section of Why Do We Fall Ill AIDS, Antibiotics, Cholera, Control of Vectors, Diarrhoea, General Prevention of Infectious Diseases, Hepatitis, Immunization, Influenza, Jaundice, Malaria, Prevention is better Than Cure, Prevention of Infectious Diseases, Proper Disposal of Waste, Rabies, Safe Drinking Water, Strong Immune System, Tuberculosis, Typhoid ,etc. have been explained. Watch the videos and master the concepts
- Sample Test(s)Test NameSubject(s)Topics / ChaptersQuestions / MarksActionTutorial - 9th - Biology [Why Do We Fall Ill II]BiologyWhy Do We Fall Ill II10 / 10View All FREE Test(s)
All organism require food. All green plants make their own food and hence are called autotrophs. All those who cannot make their own food and depend on plants are called heterotrophs. Food is the basic source of energy and we are constantly in search of methods to improve food production. In this section Improvement in Food Resources Abiotic factors, Advantages of high-yielding varieties, Application of fertilizers, Benefits of crop rotation, Biotic factors, Crop Diseases, Crop Improvement through Genetic Manipulation, Crop Production, Crop Rotation, Crop Seasons, Deficiency of Nutrients, Disadvantages of fertilizers, Disadvantages of high yielding varieties, Duration of Rotation, Effect of pests and crop diseases, Fumigation etc., have been explained. Watch the videos and master the concepts
- Sample Test(s)Test NameSubject(s)Topics / ChaptersQuestions / MarksActionTutorial - 9th - Biology [Improvement in Food Resources I]BiologyImprovement in Food Resources I10 / 10View All FREE Test(s)
All organism require food. All green plants make their own food and hence are called autotrophs. All those who cannot make their own food and depend on plants are called heterotrophs. Food is the basic source of energy and we are constantly in search of methods to improve food production. In this section Improvement in Food Resources Animal Breeding, Animal Feed, Apiary and honey collection, Artificial beehive, Artificial insemination Animal, Bee keeping, Breeding and lactation, Breeding of poultry, Broilers, Cattle farming Buffalo, Cattle farming cow, Colony of honeybees, Diseases and pests of poultry, Diseases of animals, Eggs, Embryo transfer, Farm management of buffalo and cows, Fish as a source of food, Fish farming, etc., have been explained. Watch the videos and master the concepts
- Sample Test(s)Test NameSubject(s)Topics / ChaptersQuestions / MarksActionTutorial - 9th - Biology [Improvement in Food Resources II]BiologyImprovement in Food Resources II10 / 10View All FREE Test(s)
Explore Concepts (Click & View)
- Cell
- Discovery of Cell

- Major Discoveries Related to Cell

- Difference between Unicellular and Multicellular Organisms

- Shape of Cell
- Size of Cell
- Functions of Cell
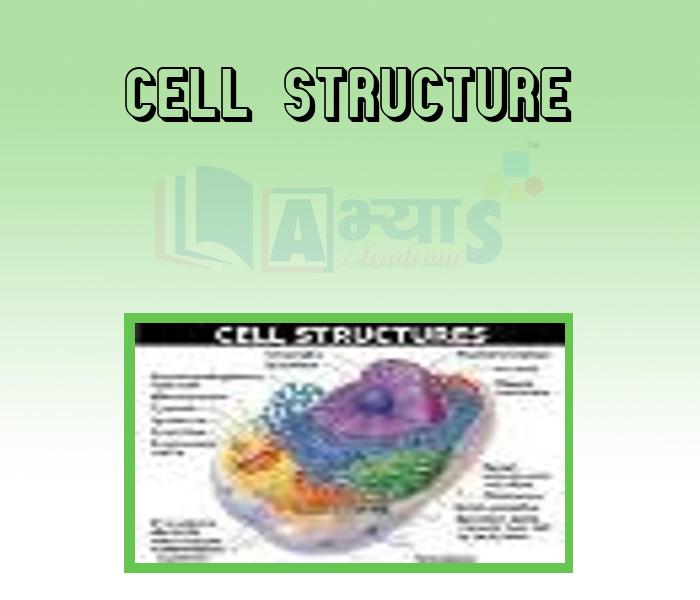
- Cell Structure
- Plasma Membrane or Cell Membrane

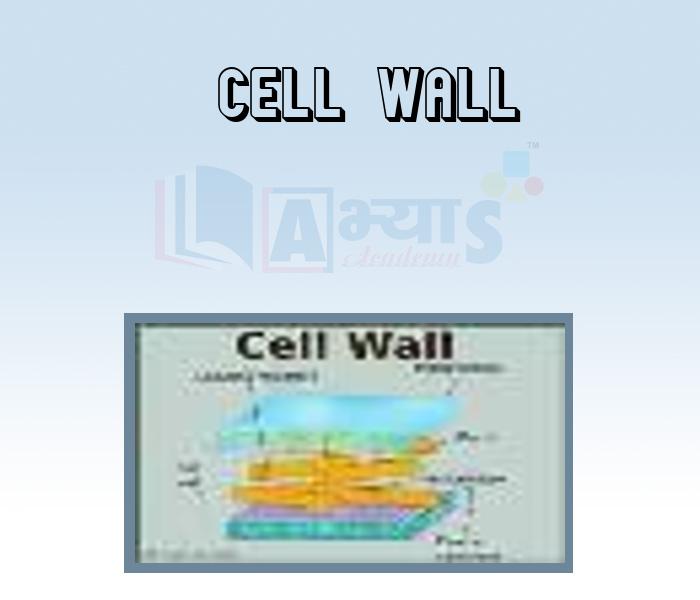
- Cell Wall
- Protoplasm

- Cytoplasm

- Function of Nucleus
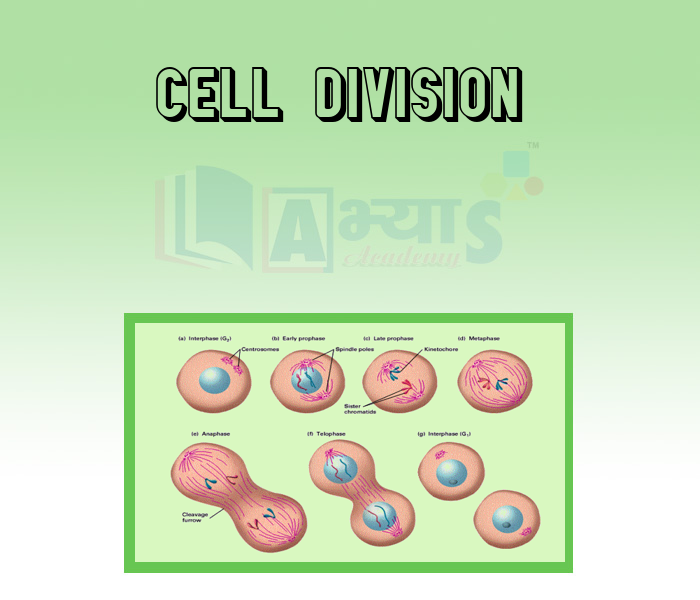
- Cell Division
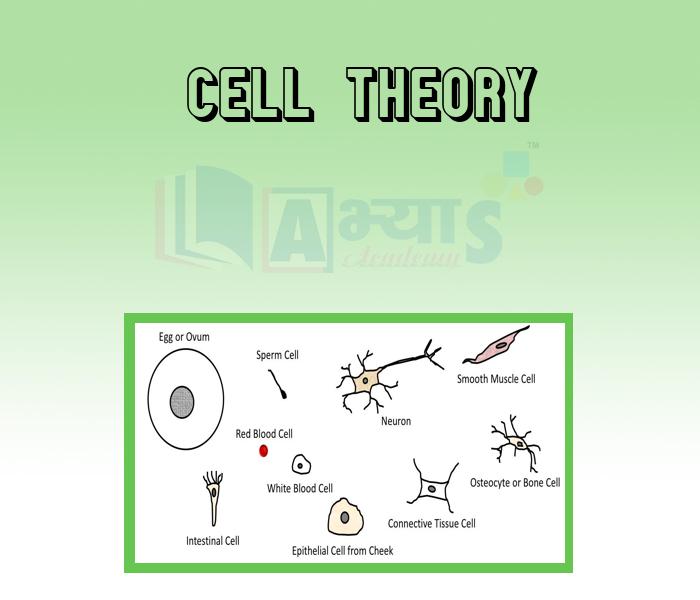
- Cell Theory
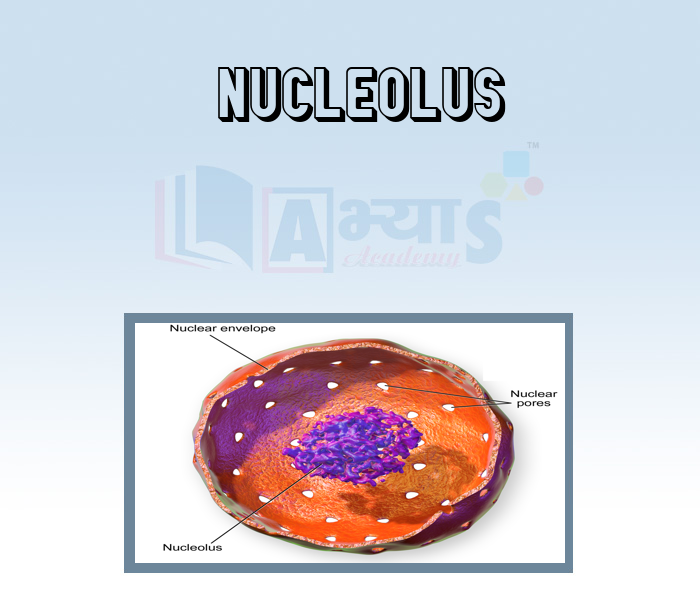
- Nucleolus
Explore Concepts (Click & View)
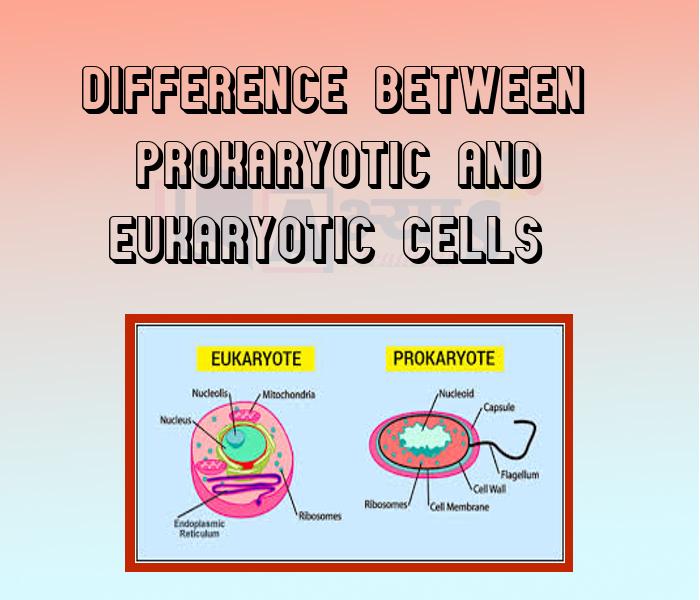
- Difference between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
- Cell Organelle

- Endoplasmic Reticulum

- Ribosomes

- Mitochondria

- Golgi body

- Plastids

- Lysosomes

- Vacuoles

- Centrosome and Centrioles

- Cytoskeleton
- Plant Cell and Animal Cell

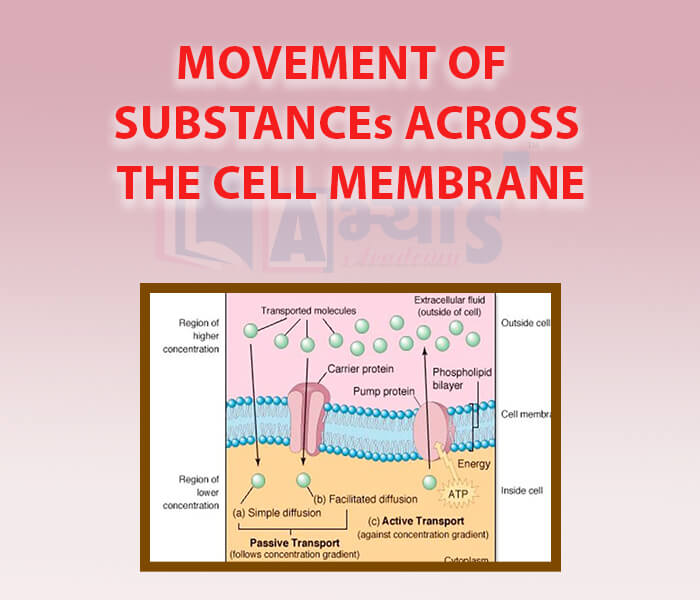
- Movement Of Substances Across The Cell Membrane
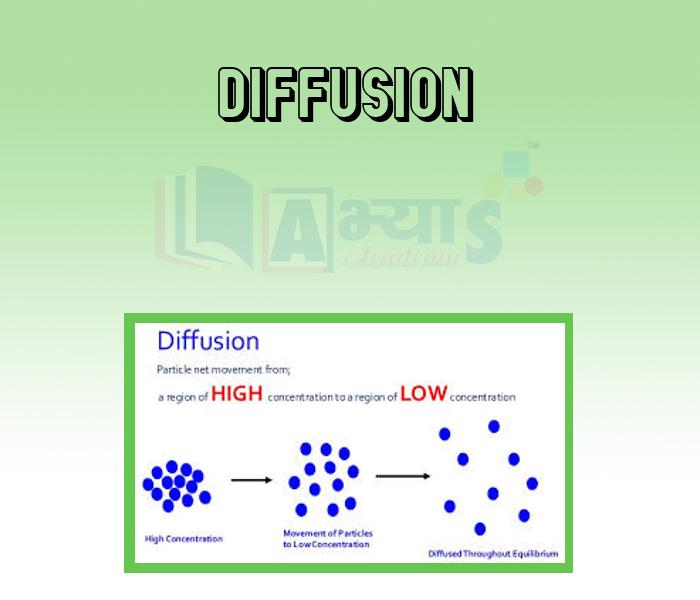
- Diffusion
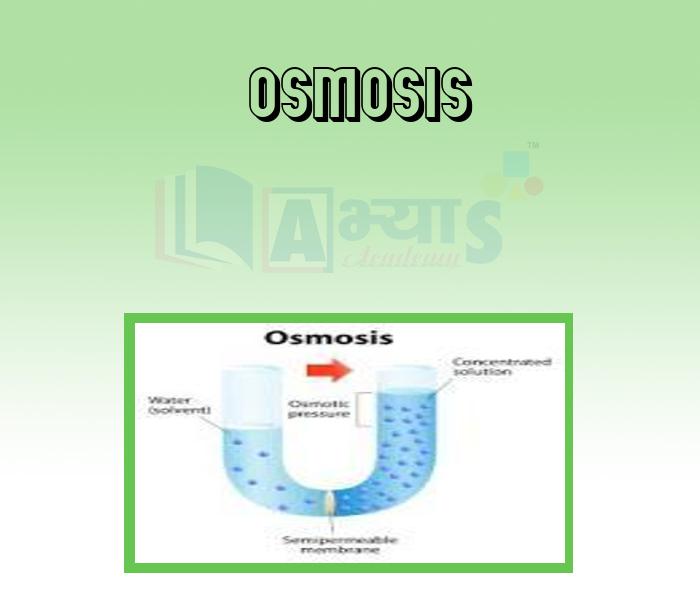
- Osmosis
- Transport of water between cells and their environment

- Demonstration of osmosis in an egg

- Demonstration of osmosis in raisins

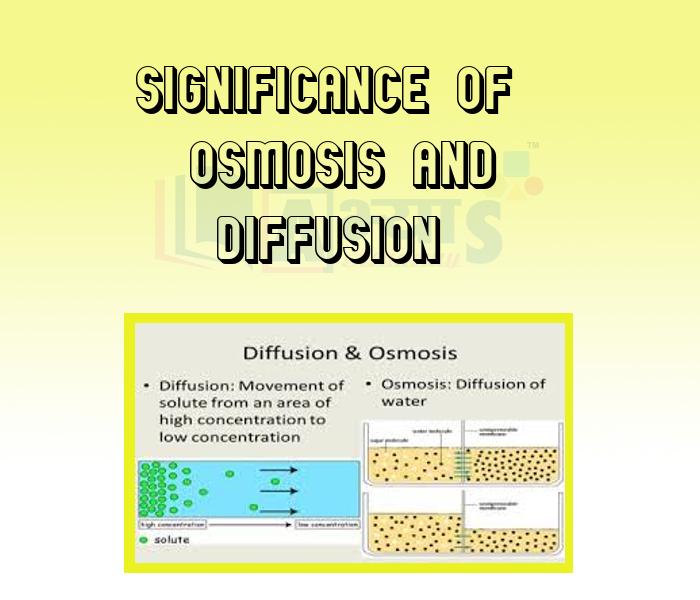
- Significance of Osmosis and Diffusion
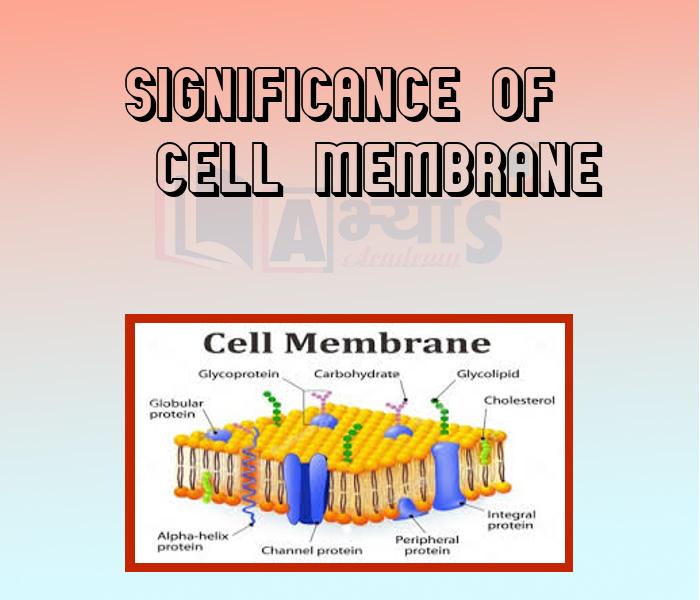
- Significance of Cell Membrane
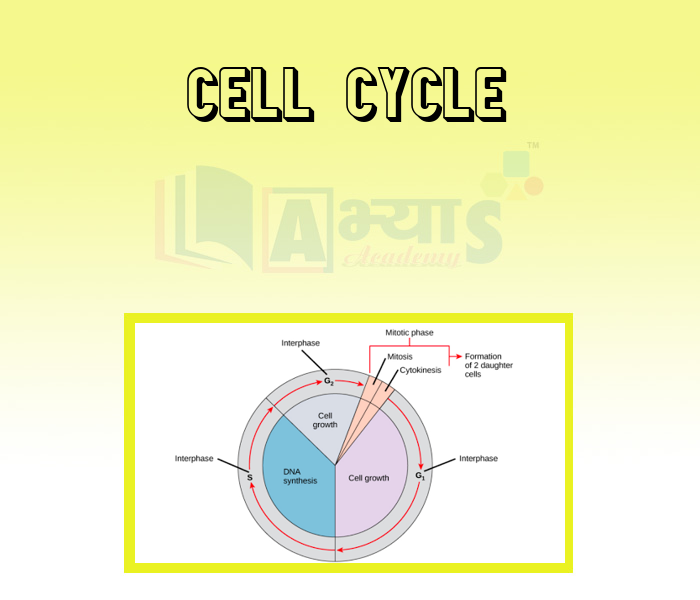
- Cell Cycle
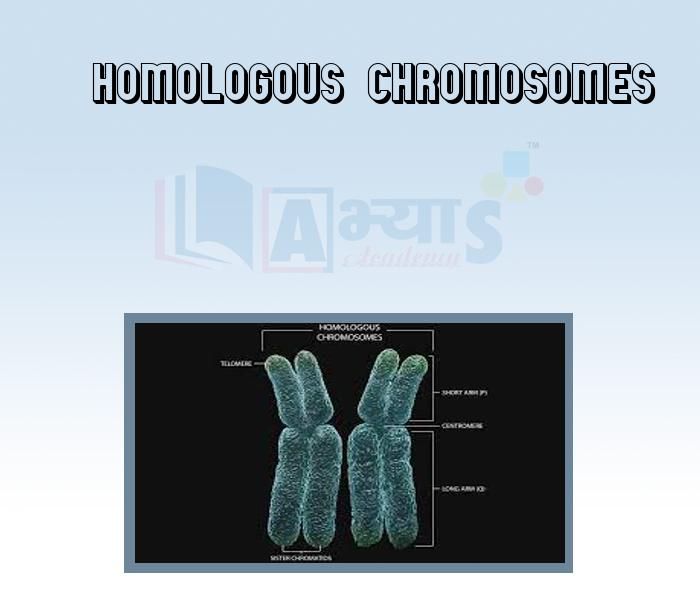
- Homologous Chromosomes
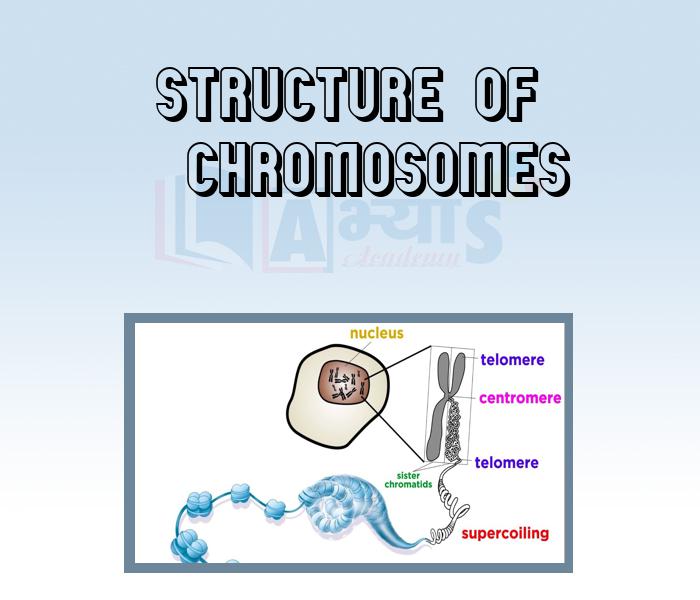
- Structure of Chromosomes
Explore Concepts (Click & View)
- Unicellular and Multicellular

- Organization of the animal body

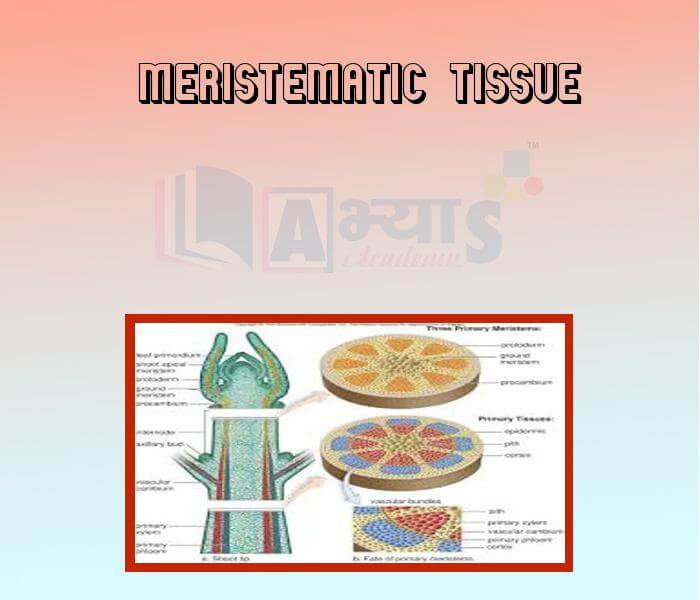
- Meristematic Tissue
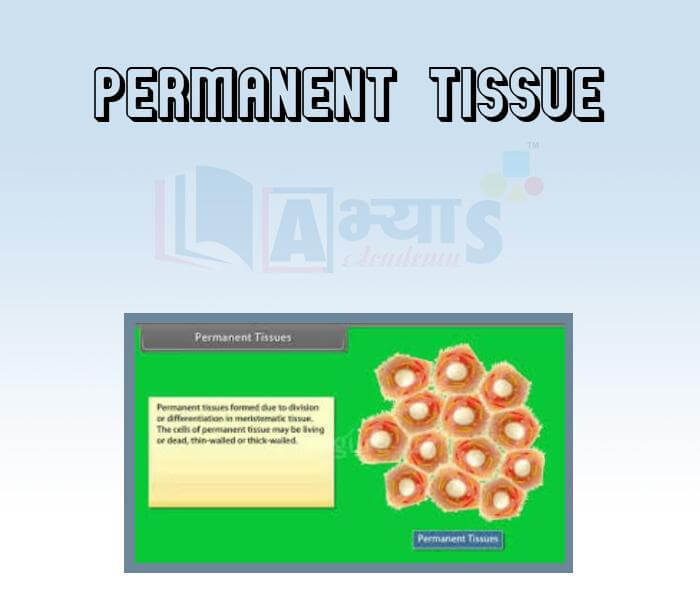
- Permanent Tissue
- Parenchyma -

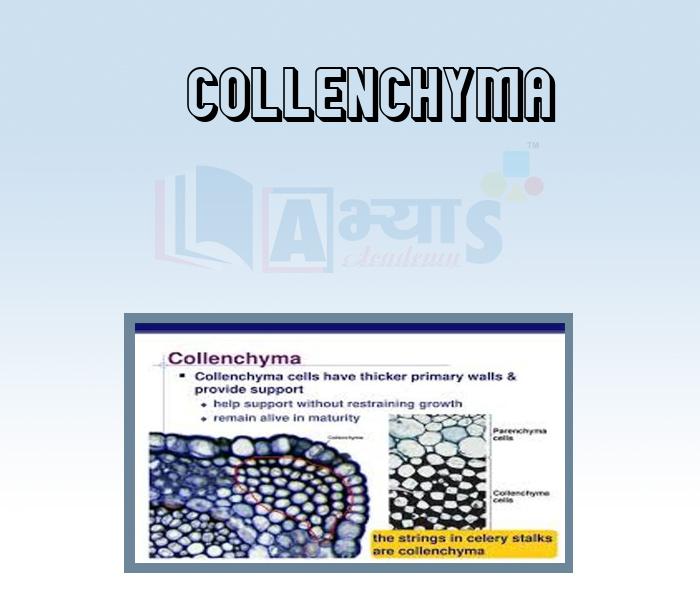
- Collenchyma
- Sclerenchyma

- Epidermis

- Xylem -

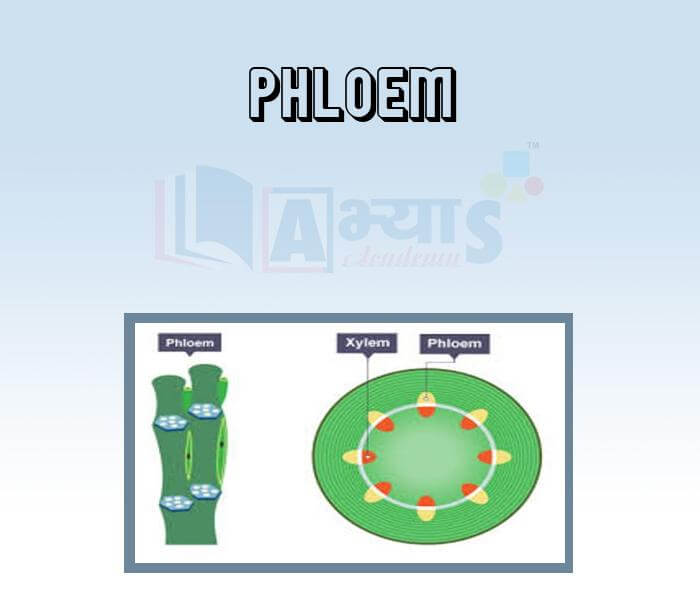
- Phloem
- Special Tissues
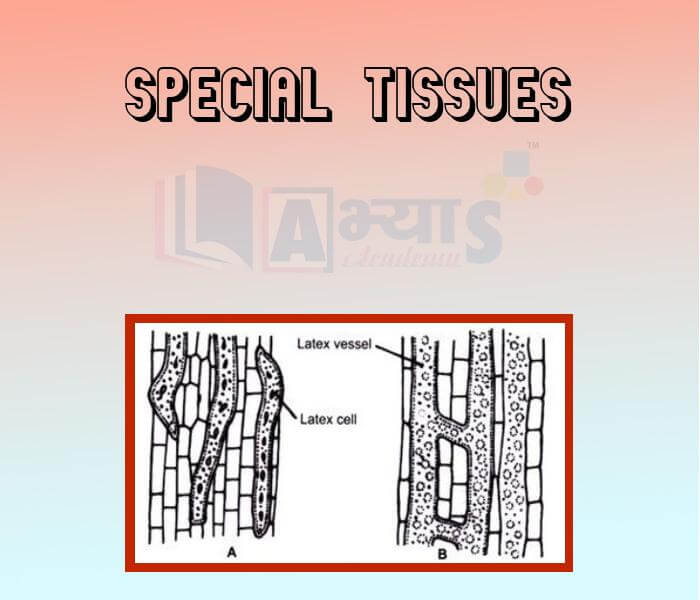
Explore Concepts (Click & View)
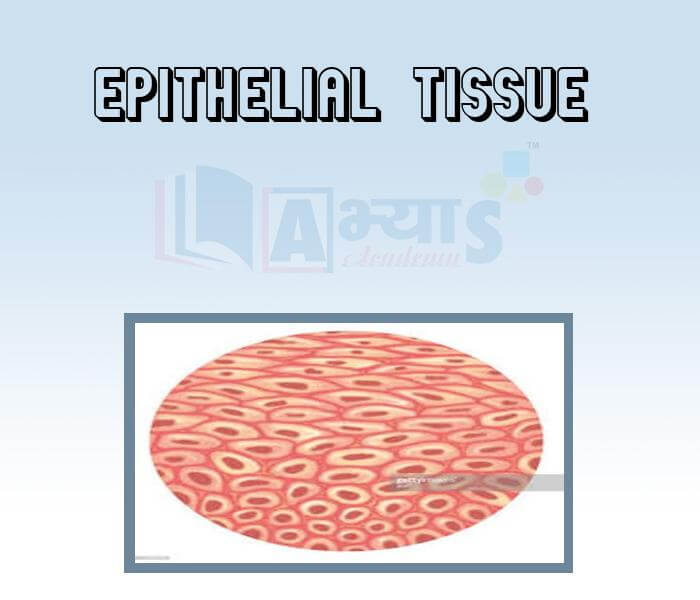
- Epithelial tissue
- Connective tissue

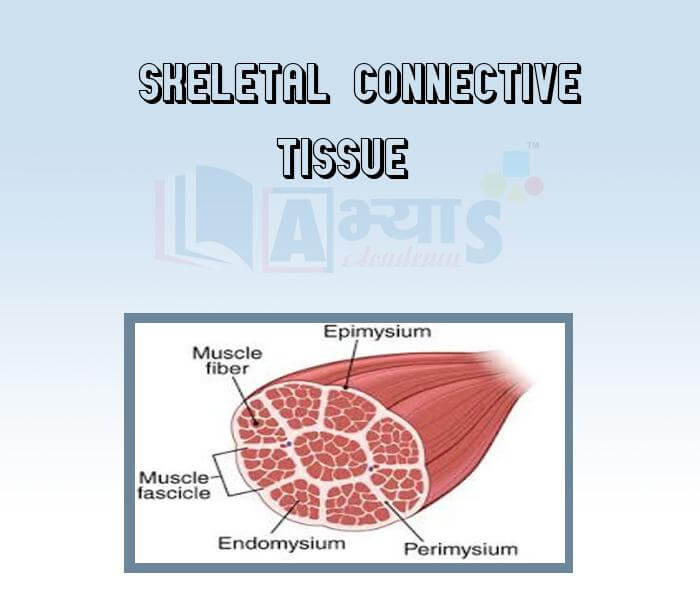
- Skeletal Connective Tissue
- Fluid Connective Tissue
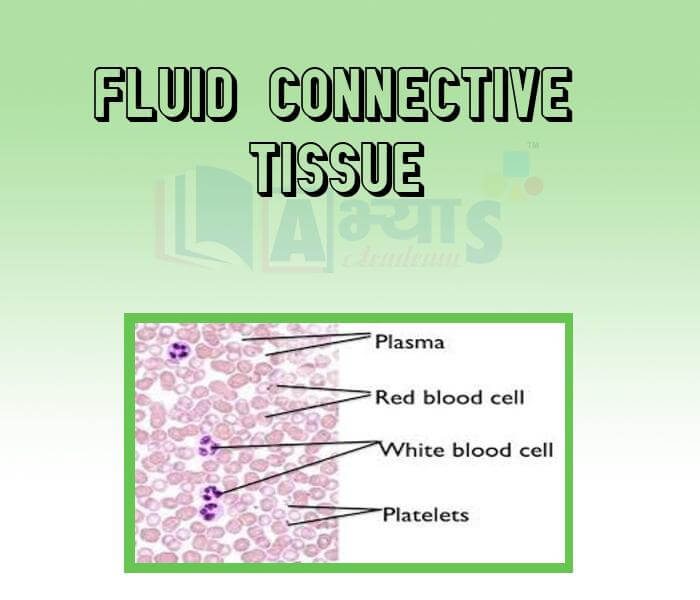
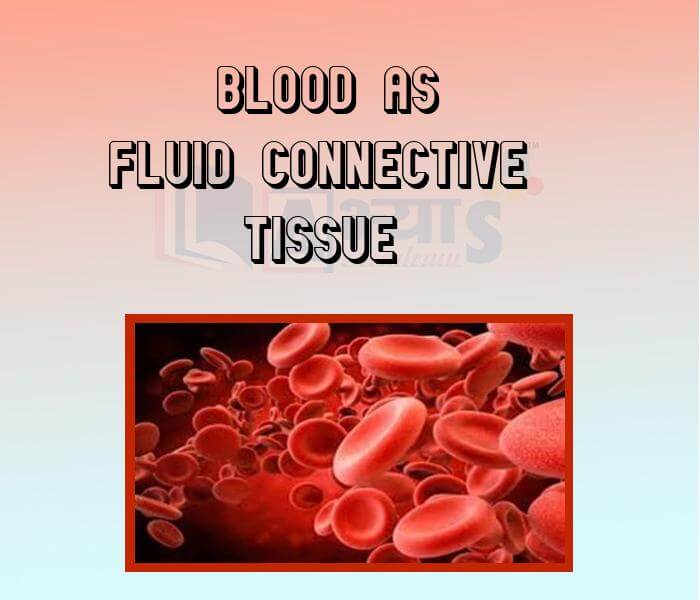
- Blood as Fluid Connective Tissue
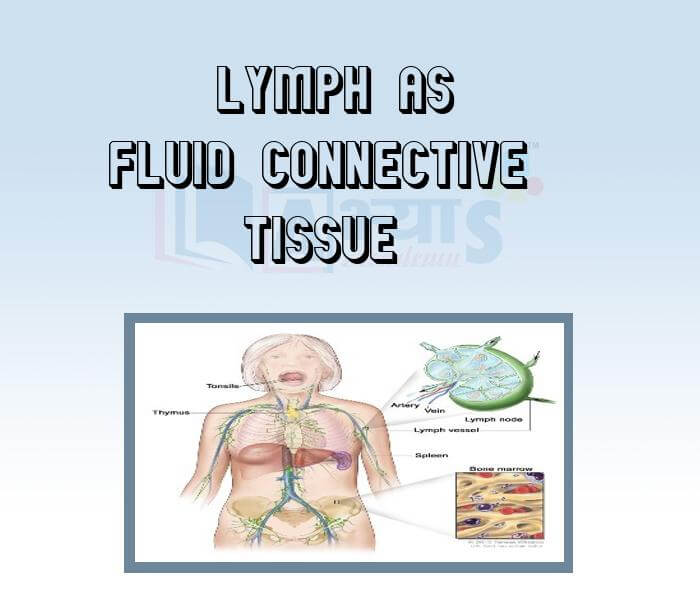
- Lymph as Fluid Connective Tissue
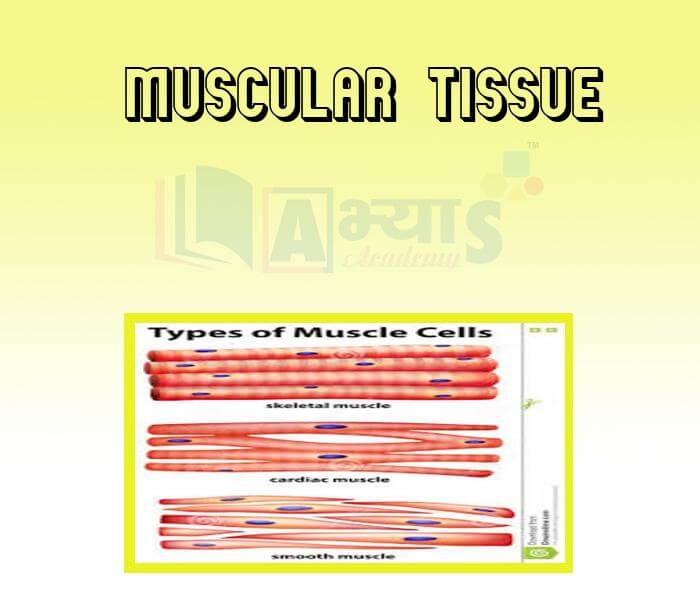
- Muscular tissue -
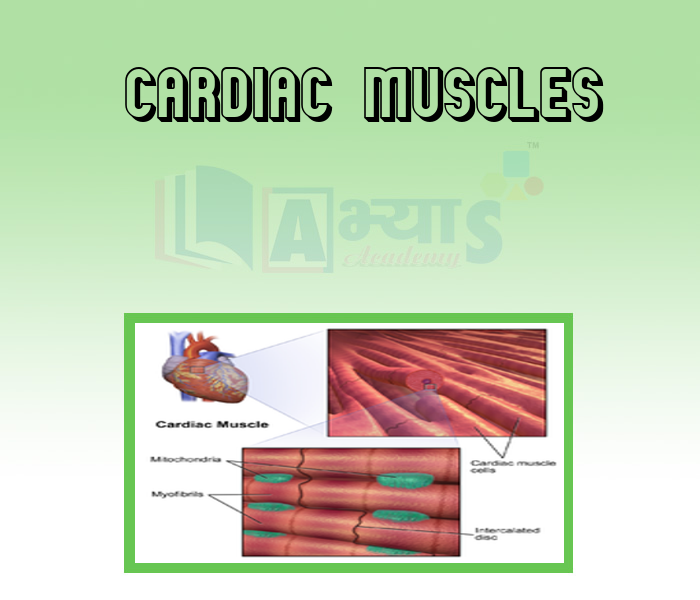
- Cardiac Muscles
- Nervous tissue
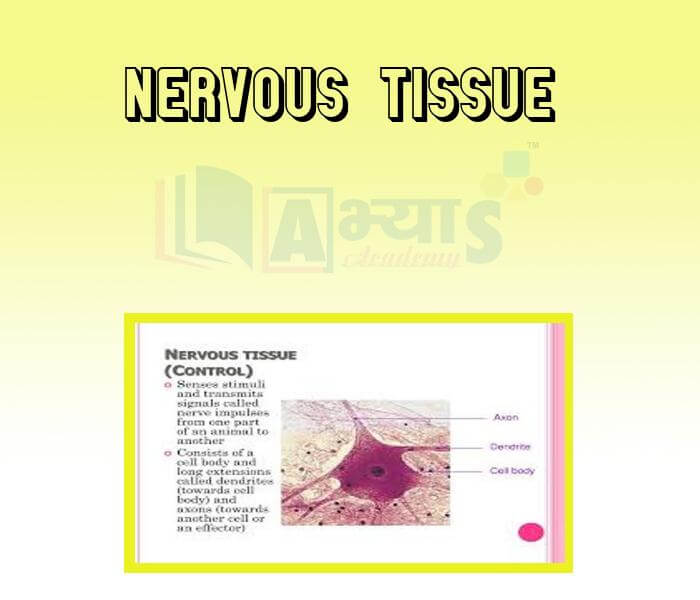
Explore Concepts (Click & View)
- Classification
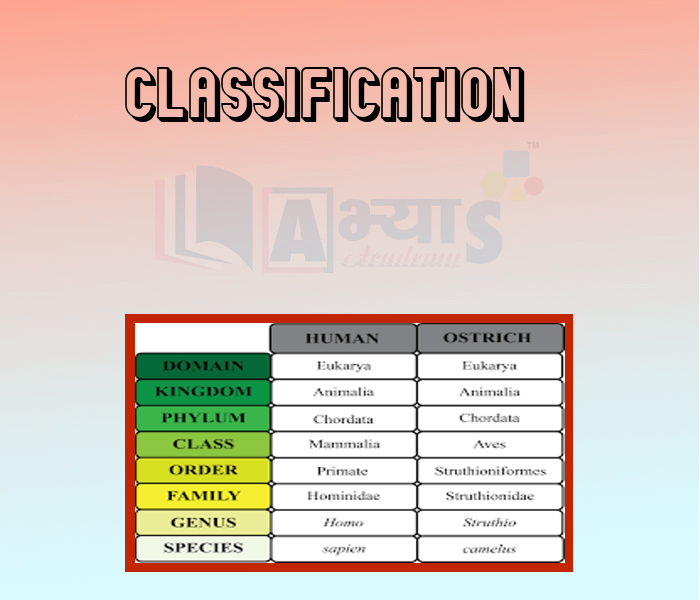
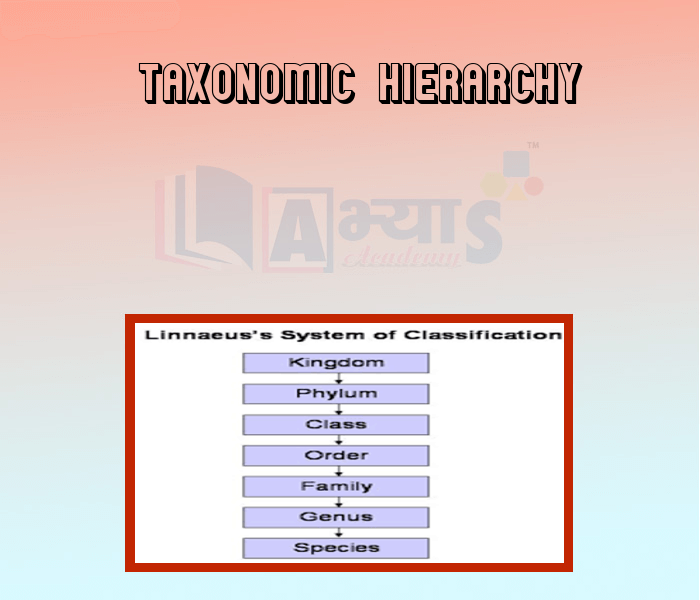
- Taxonomy -

- Taxonomic Hierarchy
- Systems of Classification and Evolution
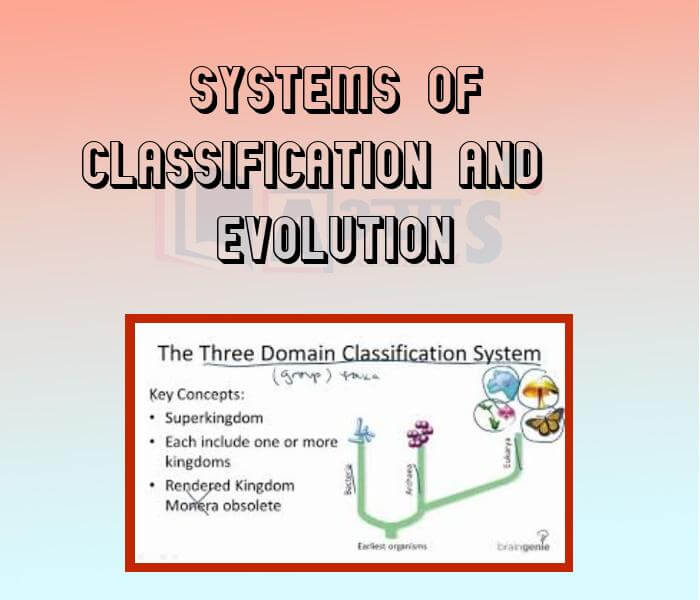
- Classification Depending on Evolution

- Charles Darwin

- Monera

- Bacteria

- Protista

- Fungi

- Plantae

- Animalia

- Thallophyta

- Algae
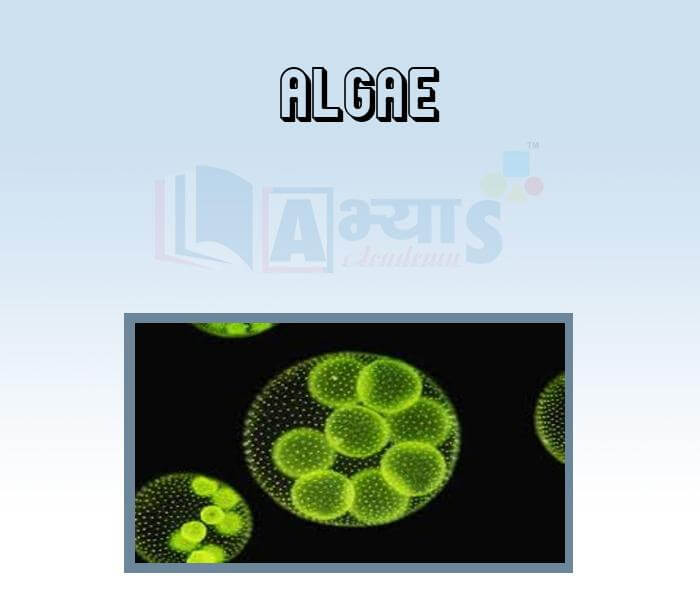
- Bryophyta

- Pteridophyta

- Gymnosperms

- Angiosperms

- Monocotyledons and Dicotyledons

Explore Concepts (Click & View)
- Phylum Porifera

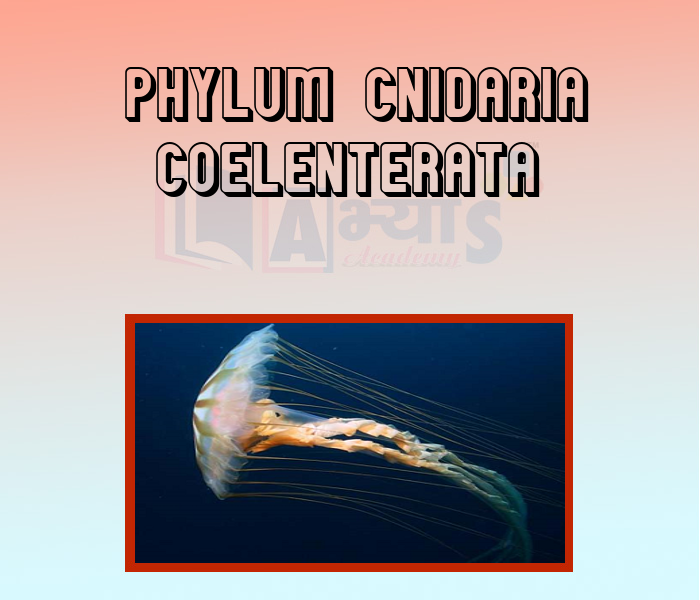
- Phylum Cnidaria Coelenterata
- Phylum Platyhelminthes

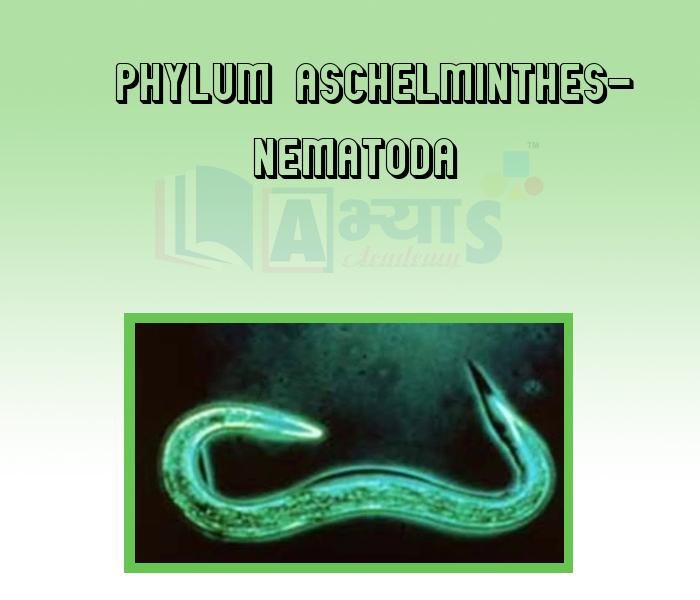
- Phylum Aschelminthes- Nematoda -
- Phylum Annelida

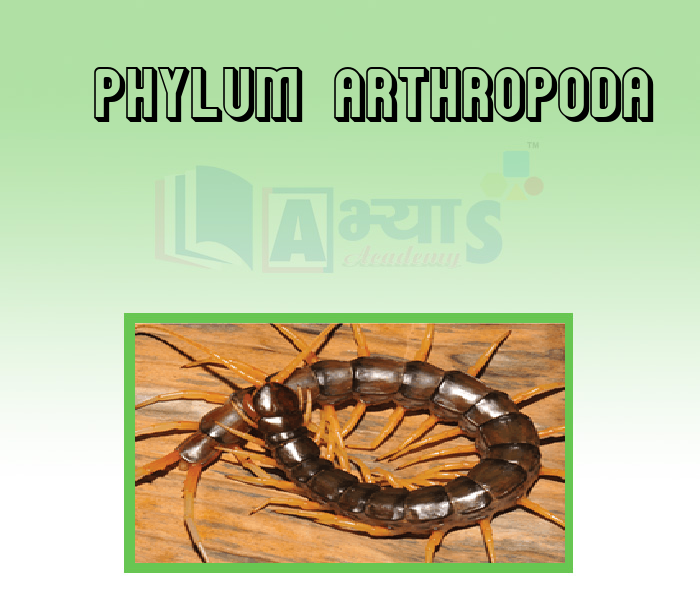
- Phylum Arthropoda

- Viruses

Explore Concepts (Click & View)
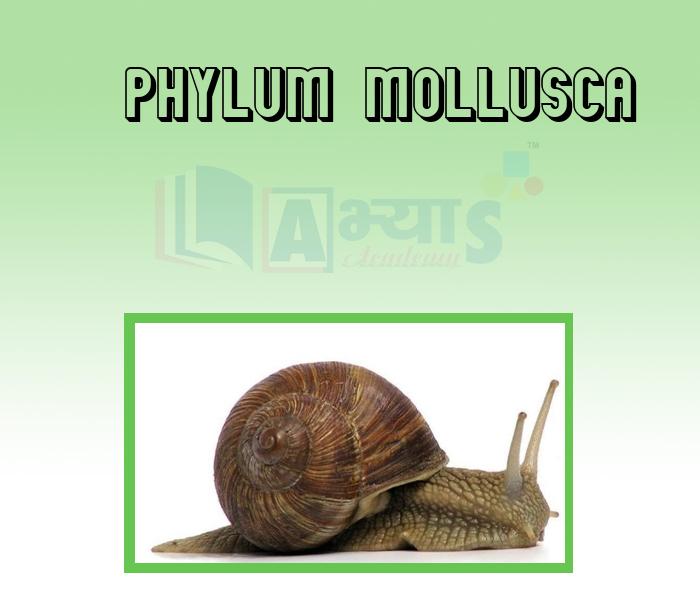
- Phylum Mollusca

- Phylum Echinodermata -

- Phylum Hemichordata

- Phylum Chordata

- Subphylum Urochordata Protochordata

- Subphylum Cephalochordata Protochordata

- Subphylum Vertebrata

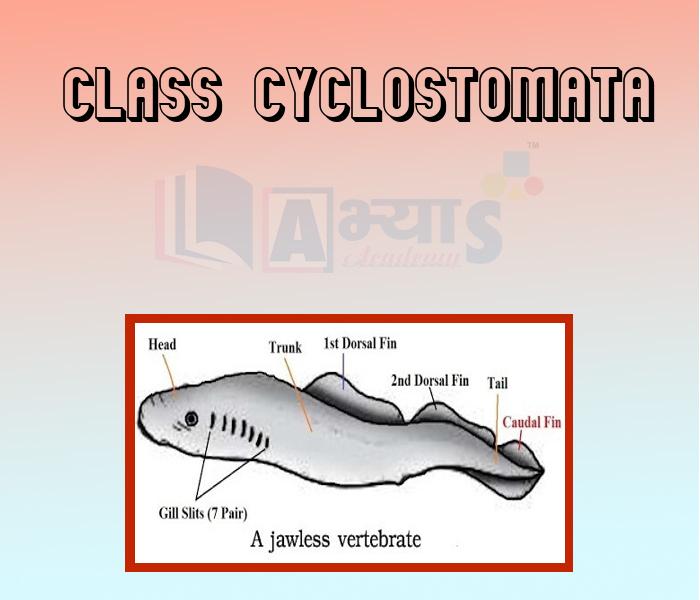
- Class Cyclostomata
- Class Chondrichthyes

- Class Osteichthyes -

- Class Amphibia

- Class Reptilia

- Class Aves

- Class Mammalia

Explore Concepts (Click & View)
- Good Health

- Basic Conditions of Good Health

- Balanced Diet

- Personal Hygiene

- Clean Surroundings

- Clean Food and Water

- Clean Air

- Exercise and Relaxation

- No Addiction

- Good Economic Conditions

- Diseases

- Signs and Symptoms of a Disease
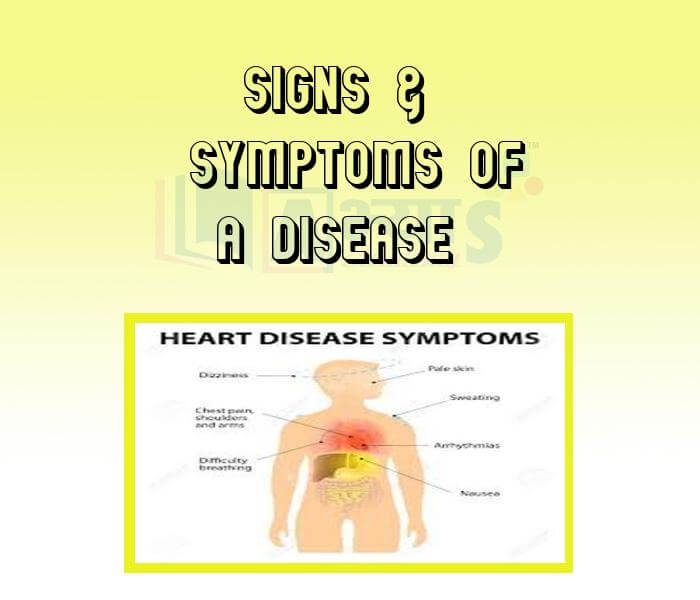
- Acute and Chronic Diseases -

- Causes of Diseases -

- Infectious Diseases

- Spreading of Communicable Disease

- Spreading of Communicable Disease Through Air

- Spreading of Communicable Disease Through Food and Water

- Spreading of Communicable Disease Through Contact

- Spreading of Communicable Disease Through Body Fluids

- Spreading of Communicable Disease Through Vectors

- Effects of Infectious Diseases -

- Treatment of Infectious Diseases -

- Eliminating Infectious Agents
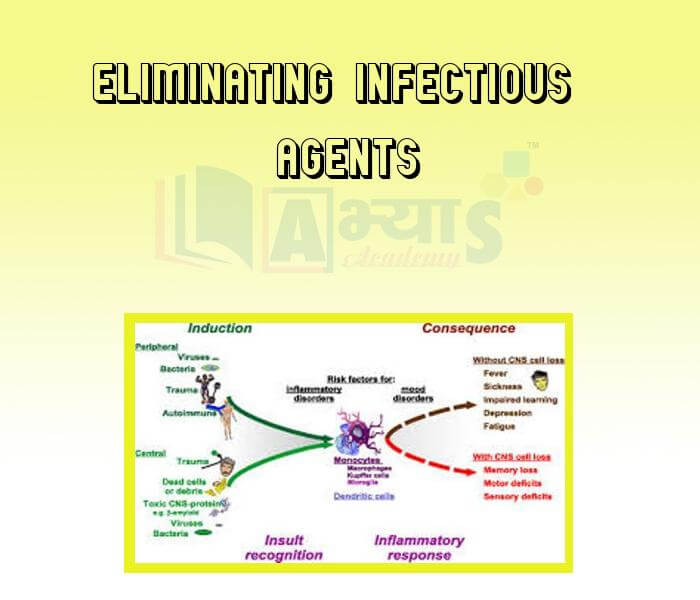
Explore Concepts (Click & View)
- Prevention is better Than Cure

- General Prevention of Infectious Diseases

- Safe Drinking Water

- Proper Disposal of Waste

- Control of Vectors

- Strong Immune System

- Prevention of Infectious Diseases

- Immunization

- Antibiotics

- Malaria

- Diarrhoea -

- Cholera
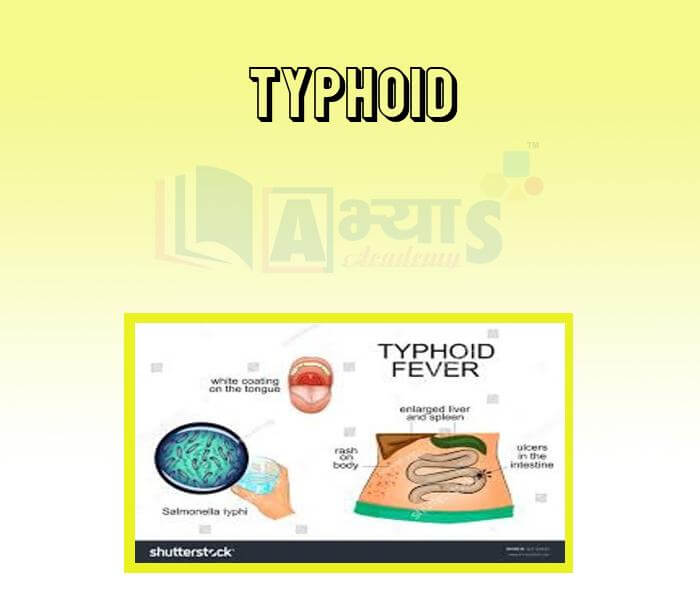
- Typhoid
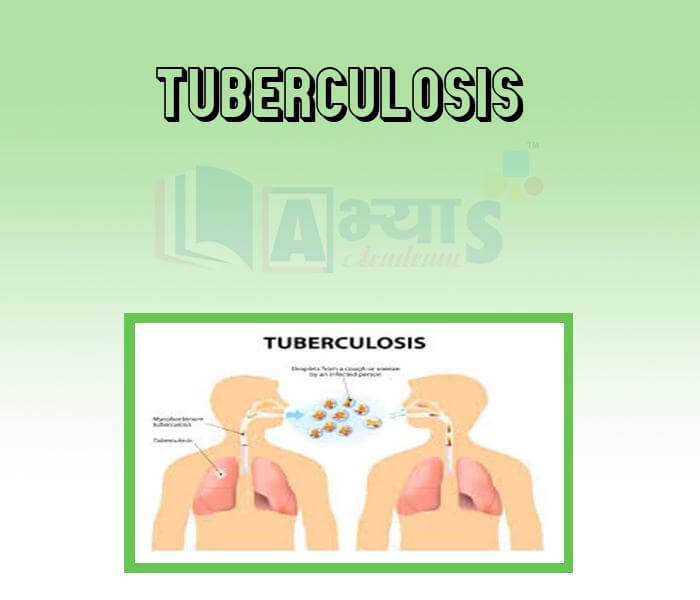
- Tuberculosis
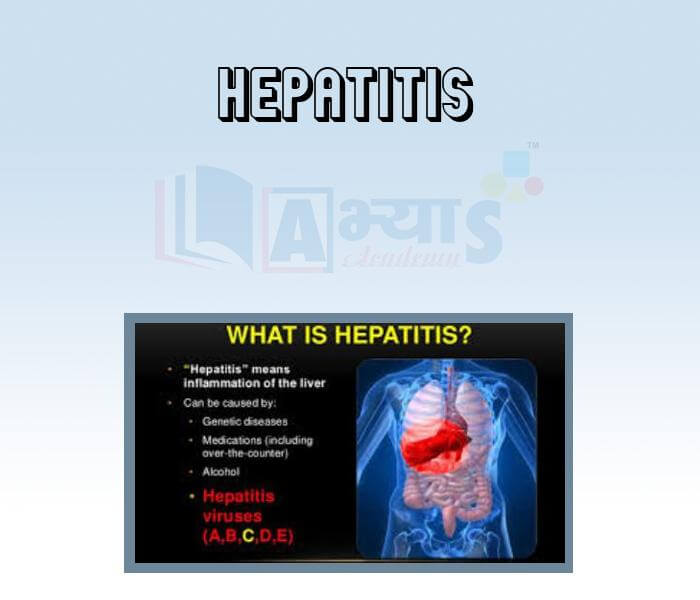
- Hepatitis
- Influenza
- Rabies -

- AIDS
- Jaundice -

- Fighting Viruses

- Antiviral Drugs

- Nanomedicines
- Tetanus
- Antiseptics and Disinfectants

- Antitoxin

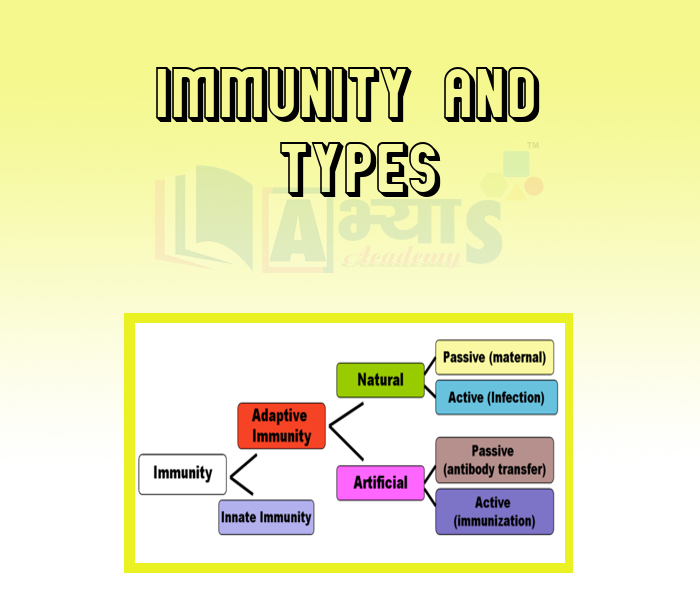
- Immunity And Types
- Serum

- Ascariasis
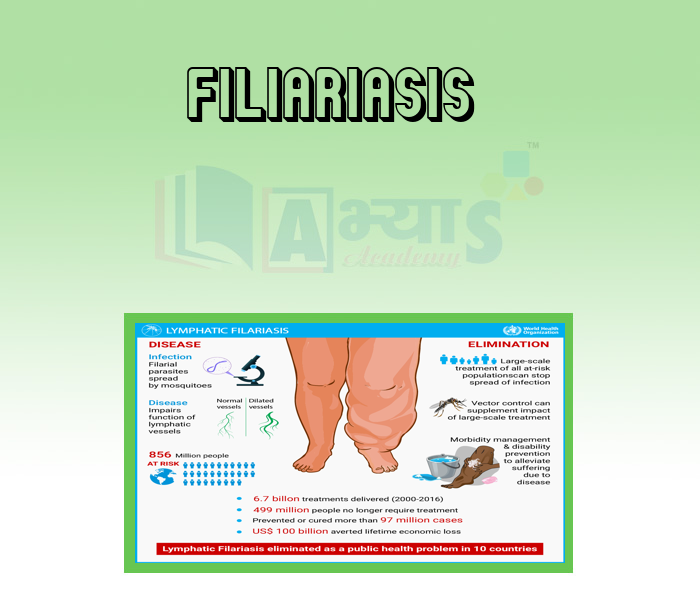
- Filiariasis
- Health Organisation

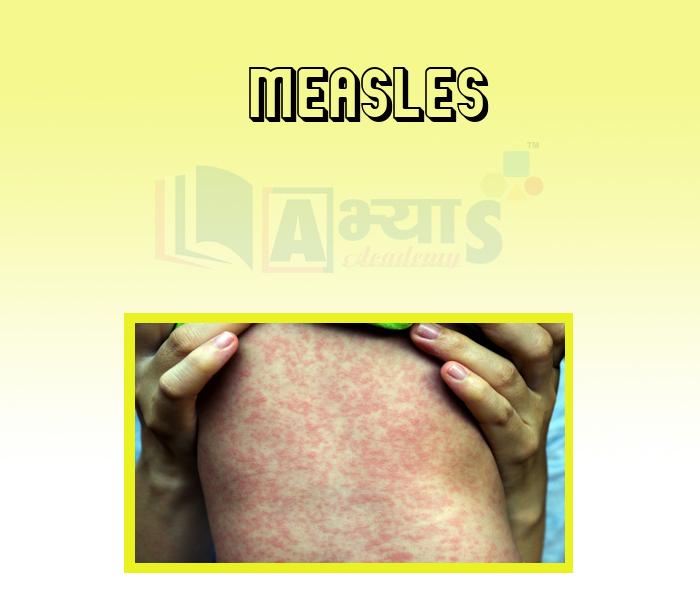
- Measles
- Chickenpox

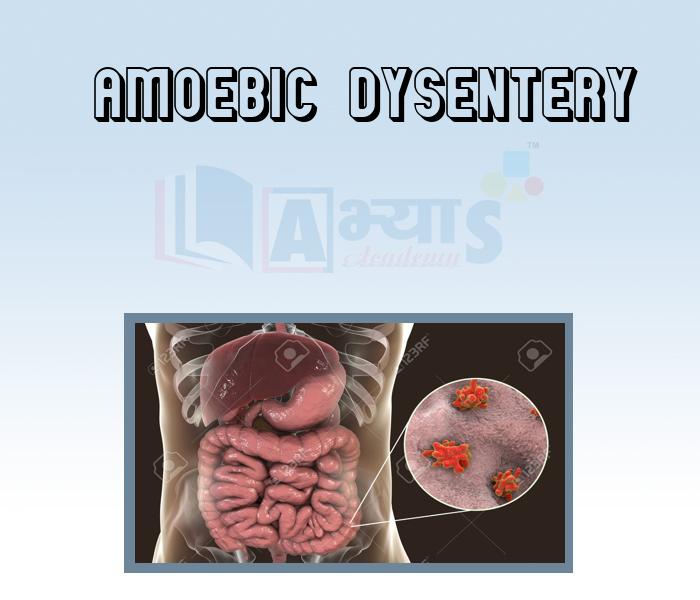
- Amoebic Dysentery
- Local Defence System

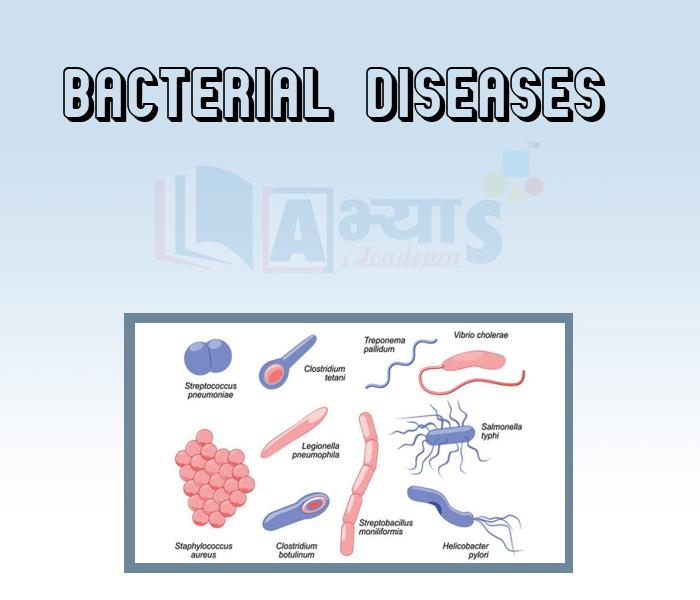
- Bacterial Diseases
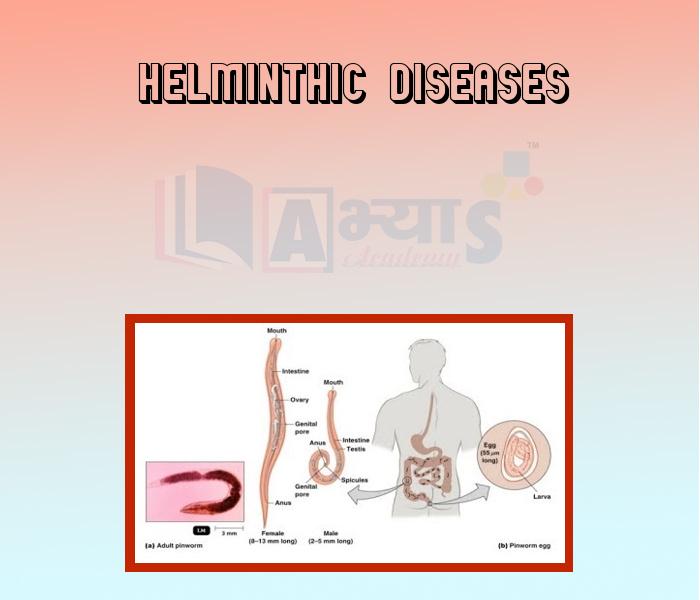
- Helminthic diseases
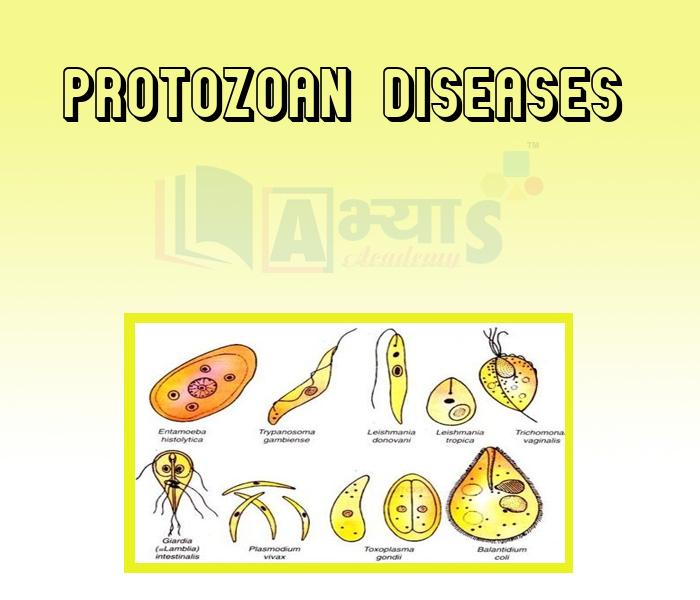
- Protozoan diseases
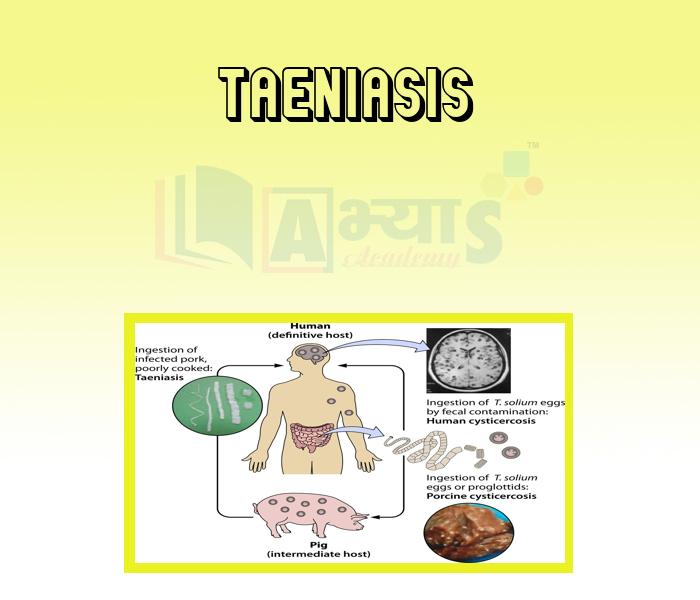
- Taeniasis
- Viral diseases

Explore Concepts (Click & View)
- Sustainable agriculture

- Crop Production

- Crop Seasons

- Kharif Crops

- Rabi Crop

- Summer crops

- Improvement in Crop Yield

- Management of Crop Production

- Methods of Crop Improvement

- Management of Nutrients

- Macronutrients
- Sources of nutrients

- Deficiency of Nutrients

- Manure and Fertilizers

- Application of fertilizers

- Judicious use of Fertilizers

- Disadvantages of fertilizers

- Organic farming

- Irrigation For Better Crop

- Mixed Cropping

- Importance of Mixed Cropping

- Intercropping

- Crop Rotation
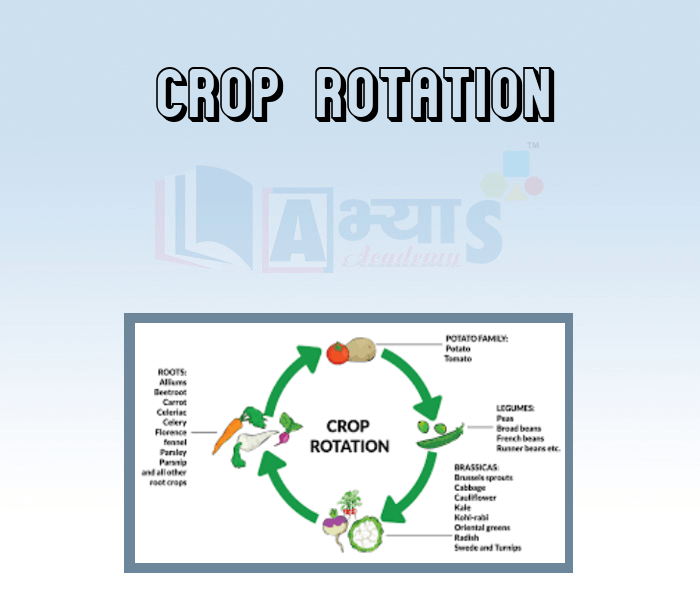
- Benefits of crop rotation

- Duration of Rotation

- Crop Improvement through Genetic Manipulation

- Variation of crops

- Plant Breeding

- Advantages of high-yielding varieties

- Disadvantages of high yielding varieties

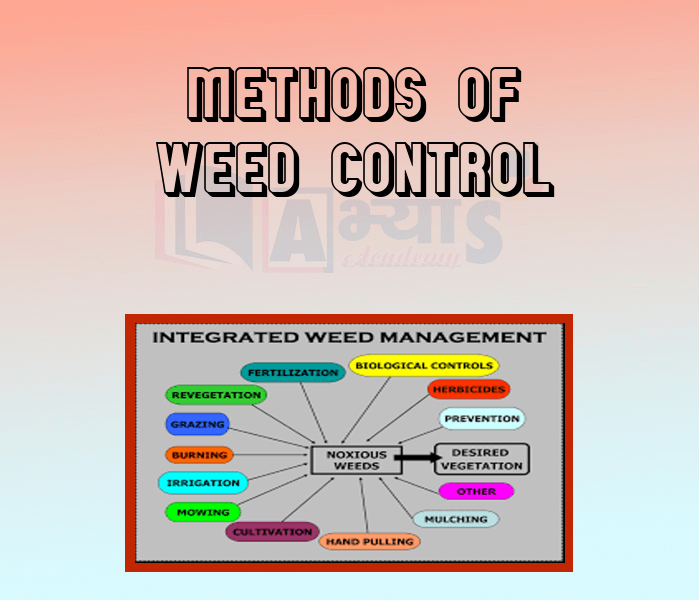
- Methods of Weed Control
- Crop Diseases

- Effect of pests and crop diseases

- Methods of Pest Control

- Harmful effects of pesticides

- Scientific storage of Grain

- Abiotic factors

- Biotic factors
- Preventive and Control Measures for Crop

- Spraying

- Fumigation

- Need for Safe Storage

Explore Concepts (Click & View)
- Importance of Animal Husbandry

- Cattle farming cow

- Cattle farming Buffalo

- Breeding and lactation

- Farm management of buffalo and cows

- Animal Feed

- Diseases of animals

- Poultry farming

- Breeding of poultry

- Eggs

- Housing and shelter of Animals

- Diseases and pests of poultry

- Fish farming

- Fish production

- Inland Fisheries

- Marine Fisheries

- Bee keeping

- Advantages of bee-keeping

Students / Parents Reviews [10]
It has a great methodology. Students here can get analysis to their test quickly.We can learn easily through PPTs and the testing methods are good. We know that where we have to practice

Barkha Arora
10thAbhyas is a complete education Institute. Here extreme care is taken by teacher with the help of regular exam. Extra classes also conducted by the institute, if the student is weak.

Om Umang
10thMy experience with Abhyas academy is very good. I did not think that my every subject coming here will be so strong. The main thing is that the online tests had made me learn here more things.

Hiya Gupta
8thBeing a parent, I saw my daughter improvement in her studies by seeing a good result in all day to day compititive exam TMO, NSO, IEO etc and as well as studies. I have got a fruitful result from my daughter.

Prisha Gupta
8thMy experience with Abhyas is very good. I have learnt many things here like vedic maths and reasoning also. Teachers here first take our doubts and then there are assignments to verify our weak points.

Shivam Rana
7thA marvelous experience with Abhyas. I am glad to share that my ward has achieved more than enough at the Ambala ABHYAS centre. Years have passed on and more and more he has gained. May the centre flourish and develop day by day by the grace of God.

Archit Segal
7thI have spent a wonderful time in Abhyas academy. It has made my reasoning more apt, English more stronger and Maths an interesting subject for me. It has given me a habbit of self studying

Yatharthi Sharma
10thMy experience was very good with Abhyas academy. I am studying here from 6th class and I am satisfied by its results in my life. I improved a lot here ahead of school syllabus.

Ayan Ghosh
8thOne of the best institutes to develope a child interest in studies.Provides SST and English knowledge also unlike other institutes. Teachers are co operative and friendly online tests andPPT develope practical knowledge also.

Aman Kumar Shrivastava
10thIt was a good experience with Abhyas Academy. I even faced problems in starting but slowly and steadily overcomed. Especially reasoning classes helped me a lot.












